HEXA - Suture SILK, Size 3-0, Needle 19mm, Length 18" - 3/8 Circle - # HSK-98980

9760_f.jpg)
Description
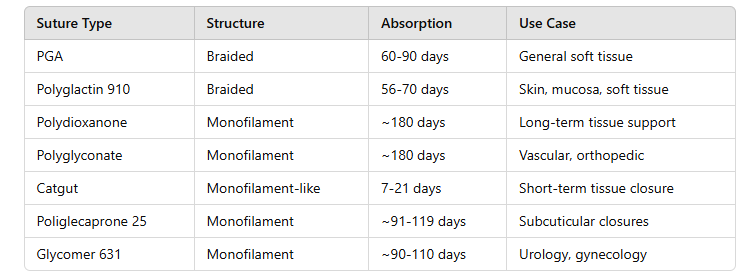
Types of Sutures by Material
- Absorbable
Sutures:
- Description:
These sutures degrade and are absorbed by the body over time.
- Examples:
- Chromic
Gut: Treated natural collagen, absorption in 10-21 days.
- Vicryl
(Polyglactin 910): Synthetic, braided, absorption in ~56-70 days.
- PDS
(Polydioxanone): Synthetic, monofilament, absorption in ~180 days.
- Monocryl
(Poliglecaprone 25): Synthetic, monofilament, absorption in ~90-120
days.
- Common
Uses: Internal tissue, gastrointestinal, gynecology, pediatrics.
- Description:
These sutures are not absorbed and may need removal or provide permanent
support.
- Examples:
- SILK:
Natural, braided, used for soft tissue approximation.
- Nylon
(Ethilon): Synthetic, monofilament, minimal tissue reaction.
- Polypropylene
(Prolene): Synthetic, monofilament, high biocompatibility.
- Polyester
(Ethibond): Synthetic, braided, durable.
- Common
Uses: Skin closures, cardiovascular, orthopedic, and long-term repairs.
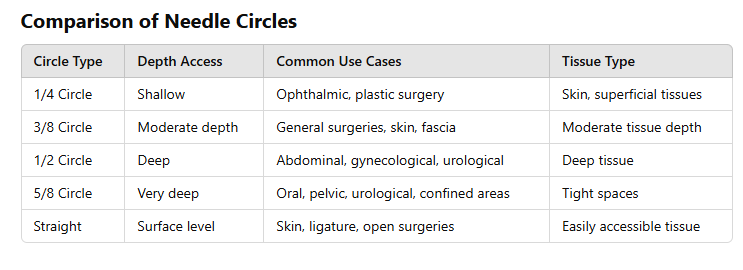
Types of Needles
- By
Shape:
- Straight
Needles: Used for superficial skin closures or easily accessible tissues.
- Curved
Needles:
- 1/4
Circle: Fine, delicate tissues.
- 3/8
Circle: Versatile, commonly used in general surgery.
- 1/2
Circle: Deep tissue suturing, abdominal closures.
- 5/8
Circle: For confined spaces (e.g., oral or urology).
- Taper
Point: Rounded tip, spreads tissue without cutting, used for soft tissue
(e.g., muscle, fascia).
- Cutting
Point:
- Regular
Cutting: Cutting edge on the inner curve, used for skin and tough
tissues.
- Reverse
Cutting: Cutting edge on the outer curve, reduces tearing in skin.
- Blunt
Point: Rounded and dull, used for friable tissues like liver or kidney.
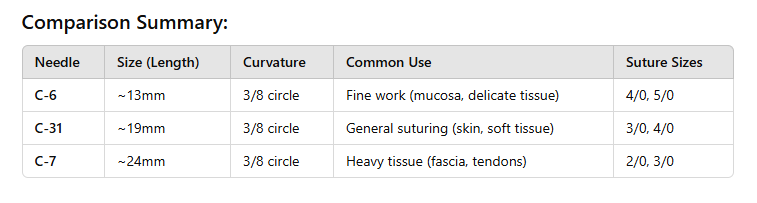
- Measured
by Length (e.g., 19mm, 24mm) and curvature (e.g., 3/8", 1/2").
- Smaller
needles (e.g., 13mm) for delicate work; larger needles for tougher
tissue.